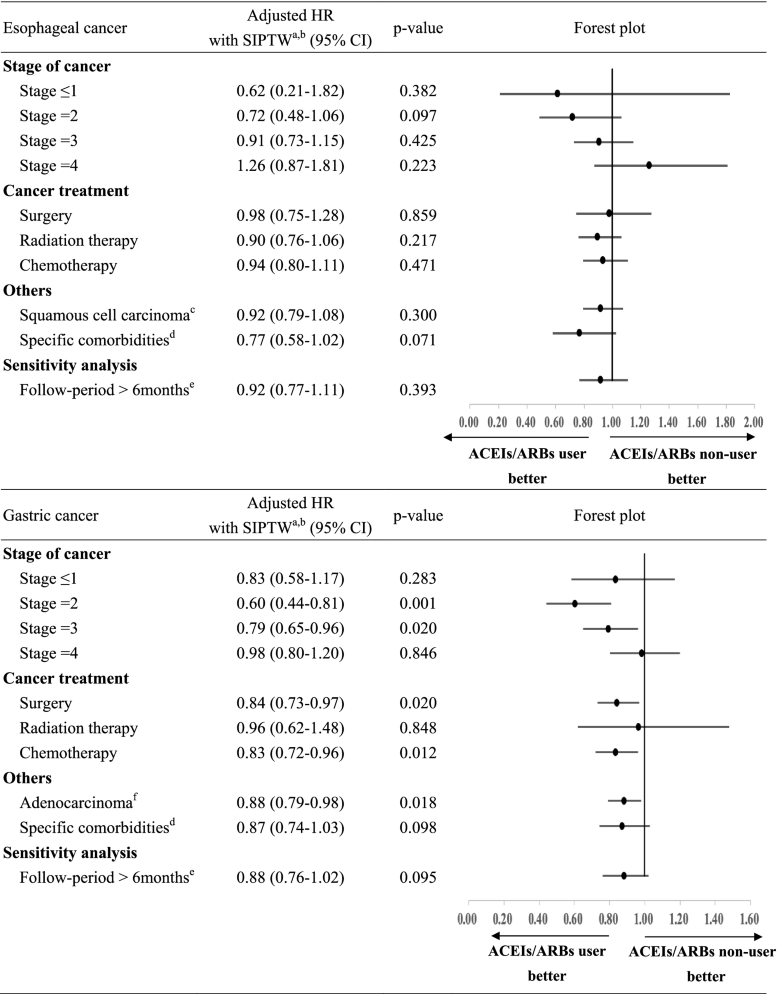
- a SIPTW Stabilize inverse probability of treatment weighting
- bAdjusted variables included age, gender, year of diagnosis, histology, cancer stage, geographic region, comorbidities (myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, mild liver disease, diabetes, moderate or severe renal disease, diabetes without chronic complication) cancer-related treatment (surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, target therapy), anti-hypertensive medication (calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, diuretics, other-classes antihypertension) and co-medication within 6 months before and after cancer diagnosis (metformin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, statins, bisphosphonates, antithrombotic agents)
- c Restricted to patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- d Restricted to patients with myocardial infarction, congestive heart disease, diabetes mellitus or diabetes mellitus with complication in the year prior to the esophageal cancer diagnosis
- e Restricted to patients who live longer than 6 months after gastric cancer diagnosis
- f Restricted to patients with gastric adenocarcinoma

